Anomers
Epimers
Glyceraldehydes
Sucrose
Aglycone
Streptomycin
1,6- glycosidic bond
Insulin
Hyaluronic acid
N- Acetylneuraminic acid
Hydrolysis
Carbohydrates
D- glucose
Polysaccharide
Starch
Search By Topics

Anomers
Epimers
Glyceraldehydes
Sucrose
Aglycone
Streptomycin
1,6- glycosidic bond
Insulin
Hyaluronic acid
N- Acetylneuraminic acid
Hydrolysis
Carbohydrates
D- glucose
Polysaccharide
Starch
by Dr. Ezz Atef biochemistry - 1st year medical students faculty of medicine fayoum university faculty of medicine cairo university ...

by Dr. Ezz Atef biochemistry - 1st year medical students faculty of medicine fayoum university facul

In this video, we start looking at carbohydrate molecules. We look at what is meant by a monosacchar

Carbohydrates: Monosaccharides in a Snap! Unlock the full A-level Biology course at http://bit.ly/2B
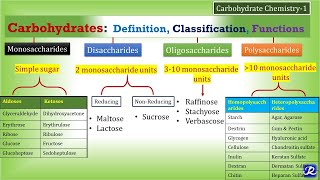
Carbohydratechemistry #njoybiochemistry Reference: Vasudevan Textbook of Biochemistry 9th edition Pa
!Disclaimer:The videos displayed above are dynamically synced using youtube search api as per the content of this page and are for educational purposes only. We are not the creater of any videos displaying here. The credits and rights goes to the respective creaters/channel-owners on Youtube. .
Triacylglycerolds
2 of 15 〉 The isomerism associated with unsaturated fatty acidsGeometric isomerism (cis-trans isomerism)
13 more 👇
ΔG = ΔH – TΔS (T = Absolute temperature)
2 of 15 〉 A negative sign of free energy indicates that the reaction isExergonic or spontaneous
13 more 👇
β-Glycosidic bonds
2 of 15 〉 The most important carbohydrate associated with flatulence caused by ingestion of leguminous seedsRaffinose
13 more 👇
0 likes 852 views
 Interesting facts about Carbohydrates
Interesting facts about Carbohydrates