Motion :
- We classify things on different basis and among all of them there is basis of speed which have further two simple categories. When the position of object is constant i.e. rest and the other is when there is movement of object from one position to another position with respect to the observer i.e.
- Rest: A stationary building, a tree, a static bench and so on are some of the things that are usually found still so it’s clear that any object which is not moving and changing its position in respect of time, distance and observer are said to be at rest.
- Motion: A moving car, a flying bird, a moving vehicle, a running fan and so on are categorized as being in motion. It can also be defined as a peculiar set of reactions in which object changes its position with respect to its surrounding, distance and time.
- Rest and motion are relative states. It means an object which is at rest at one frame of reference can be in motion in another frame of reference at the same time and vice-versa. For example if a person is inside any moving vehicle, he/she will find that vehicle at rest as per their frame of reference but if a person is somewhere outside any moving vehicle, he/she will find that particular vehicle in motion as per their frame of reference. Point of Reference can be anything, be it a tree or even a person.
Notes
1. Some important definitions related to motion | Scalar and Vector Quantities
Let us discuss some important definitions related to motion.
• Reference point:
It is the point around which the location of an object is measured. It is also known as the origin.
• Scalar quantity:
This physical quantity has its own magnitude but not specific direction. Example- distance, speed etc.
• Vector quantity :
This physical quantity has both magnitudes as well as specific direction. Example – displacement, velocity, etc.
• Distance :
1. The actual path or length covered by a body during its journey from the initial position to the final position.
2. It’s a scalar quantity
3. Ex – Rohan travelled 37 km.
• Displacement :
1. The shortest possible distance covered by a body during it’s journey from the initial position to the final position.
2. It’s a vector quantity.
3. Example – Rohan travelled 37 km in South-West direction.
4. It can be zero if the initial position and final position are the same. Ex – circular motion.
• Motion can be one dimensional, two dimensional and three dimensional on the basis of direction.
One dimensional - It is also termed as motion in a straight line. When an object moves in a straight line with respect to the observer via using only one coordinate out of three.
Example: the motion of the lift, walking in Narrow Street etc.
Two dimensional – When an object moves via using two out of the three coordinates is termed as two dimensional. For example the motion of a car, the motion of rolling ball etc.
Three dimensional – When a body moves via using all the three coordinates and even movement in any direction is termed as three-dimensional motion. For example a flying kite, a moving aeroplane etc.
- Uniform motion:
When a body travels equal distance in equal interval of time .
- Non uniform motion:
When a body travels unequal distance in equal interval of time.
- Speed :
- Measurements of distance travelled per unit time .
- Speed – distance travelled / time taken.
- V – S / T
- I unit – meter / sec i.e., m/s
- Average speed :
Total distance travelled / total time taken.
- Velocity :
- It’s speed of the body in given direction.
- Velocity – displacement / time
- Its a vector quantity.
- Vavg ( for non uniform motion ) – total displacement / total time
- Vavg ( for uniform motion ) - initial distance (u) + final distance (v) / 2 or u + v / 2
- S I unit of velocity – ms -1
- It can be positive, negative or zero.
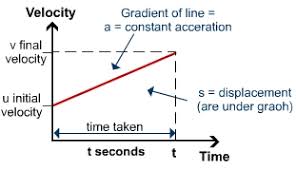
- Acceleration :
- It is seen in non uniform motion and it can be defined as the rate of change of velocity per unit time.
- Acceleration (a) = change in velocity (v – u) / t
- a = v – u / t
- If v > u then (a) will be positive.
- If u > v then (a) will be negative.
- Deaceleration : a = v – u / t
- Equation of motion for uniformly accelerated motion:
- First equation :
v – u + at
Final velocity = initial velocity + acceleration × time
- Second equation :
S = ut + ½ at2
- Third equation :
V2 = u2 + 2as
2. Types Of Motion in Physics

Types of motion :
Motion can take place anywhere and in any way. To make it more specific in terms of its category, it is being classified into four different types i.e., translational, rotational, periodic and non-periodic.
- Translational motion:
- This motion is a kind of motion in which an object moves from one point to another uniformly in the same line or direction.
- For ex – a man walking on the street, train moving on track, a child going down a slide, etc.
- It is further divided into two types:
- Rectilinear motion:
- When an object moves in a straight line.
- Ex – vehicle moving on the straight road.
- Curvilinear motion:
- When an object moves along the circular path.
- Ex – Car taking a turn.
- Rotational motion:
- This motion is a kind of motion in which an object moves around an axis with its different parts moves by different distances with an equal interval of time.
- For example – a rotating fan, moving blades of a windmill, rotation of the earth etc.
- Periodic motion:
- This motion is a kind of motion that repeatss itself in a regular interval of time.
- For ex- rotation of earth, the hands of a clock, blades of fan, etc.
- Non-Periodic motion:
- This motion is a kind of motion that does not repeat itself in a regular interval of time or a kind of motion that does not repeat itself at all.
- For ex – a bird gliding in the sky, children playing in the park, car moving on road etc.
3. Three Laws of Motion

In this part we are going to discuss about the Newton’s three laws of motion.
As we all know Motion is a kind of state in which some distance is being covered with respect to the time that possesses some speed. We have a well-flourished generation that believes in science and technology which is purely adapted from somewhere who is none other then but our respective and intelligent scientists who did a lot of inventions to make our life easy and fruitful.
Laws of motion, also known as Newton’s three Laws of Motion.
- First law motion:
- Every object persists in the same state as it is, either at rest or motion until an external force is applied to it.
- It is also known as the Law of Inertia because this shows the property of massive change in the states of motion.
- It was discovered by Galileo.
- It simply means that an object can’t start, stop or change direction by themselves, it needs some external force to do that so.
- The second law of motion:
- Force equals mass times acceleration (F = ma), where “F” is a force, “m” is mass and “a” is acceleration.
- It describes the reaction of the massive body when external for is applied to it which can add velocity, slow speed, and change direction of the stationary body.
- SI unit office in Newton.
- Third Law of motion:
- Every action has an equal and opposite reaction.
- When an object pushes a second object at a point of contact with some applied force then, there must be the equal and opposite amount of force to the first one from the second object that can cancel the applied force.
- For example – Throwing football on the ground gives the same amount of force to the ground again which results in the bouncing back of the football.
More in this Chapter..

Some important definitions related to motion | Scalar and Vector Quantities
Scalar quantity : This physical quantity have it’s own magnitude but not specific direction. Example- distance, speed etc.Vector quantity :This ph
4.37M Join the discussion.

Types Of Motion in Physics
This motion is a kind of motion in which an object moves from one point to another uniformly in the same line or direction. Translational motion.
4.37M Join the discussion.

Three Laws of Motion
Motion is a kind of state in which some distance is
being covered with respect to the time that possesses some speed. We have a well-flourished
ge
4.37M Join the discussion.
.png)



















.jpg)







 संज्ञा
संज्ञा  Cell - The Unit Of Life
Cell - The Unit Of Life