1. The idea of divisibility of matter was considered long back in India, around 500 BC.
2. The unknown and unseen form of matter was always wondered by Ancient Indian and Greek philosophers.
3. Maharishi Kanad (Indian philosopher) : He postulated that if we go on dividing matter (padarth), we shall get smaller and smaller particles. Ultimately, a time will come when we shall come across the smallest particles beyond which further division will not be possible. He named these particles parmanu.
4. Pakudha Katyayama ( Indian philosopher) : he postulated that there are various forms of matter because the particles of matter exist together in combination.
5. Ancient Greek Philosophers – Democritus and Leucippus suggested that if we go on the dividing matter, a stage will come when particles obtained cannot be further divided.
6. All these ideas were based on philosophical consideration and not much experimental work.
7. The foundation of chemical science was laid by Antoine L. Lavoisier, by establishing two important laws of chemical combination.
Notes
1. Laws Of Chemical Combination And Dalton's Atomic Theory
Laws of Chemical Combination
After much experimentations, Lavoisier and Joseph L. Proust proposed two laws of chemical combination.
1. Law of conservation of mass:
This the law states that during a chemical reaction the sum of masses of the reactant and the product remains unchanged or we can say that mass can neither be created nor destroyed. This is known as the law of conservation of mass
2. Law of constant proportion: It is also known as “the law of definite proportion”
This the law states that in a pure chemical compound elements are always present in the definite proportion by mass irrespective of where the the compound came from or who prepared it.
Dalton’s Atomic Theory:
1. The two theories proposed by Lavoisier and Joseph L. Proust lacked appropriate explanations.
2. British chemist John Dalton provided the basic theory about the nature of matter, he took the idea of divisibility of matter which was till then just a philosophy.
3. He said that the smallest particles of matter are atoms and thus, he provided an explanation for ‘the law of conservation of mass' and ‘the law of definite proportions'.
4. According to Dalton’s atomic theory, all matter, whether an element or compound or mixture is composed of small particles called atoms.
Postulates of Dalton's atomic theory:
1. Every matter is made up of very tiny particles called atoms.
2. Atoms are indivisible particles, that can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
3. Atoms of a given element are identical in mass and chemical properties.
4. The atoms of different elements has different masses and chemical properties.
5. Atoms combine in the ratio of small whole numbers to form compounds.
6. The relative number and kinds of atoms are constant in a given compound.
2. Atom, Atomic Mass, Atoms Existence And Nomenclature Of Elements
Atom:
1. Building blocks of all matter are called atoms.
2. Atoms are extremely small, they are smaller than anything that we can imagine or compare with.
3. For example – more than millions of atoms when stacked would make a layer as thick as any sheet of paper.
4. Atomic radius is measured in nanometres
1/10 9 m = 1 nm
1 m = 10 9 nm
5. Some examples of an atom – Oxygen (O), Hydrogen (H), Nitrogen (N), etc.
The naming of Atoms or Elements and Their Symbols :
1. Symbols for elements in a very specific sense was first proposed by Dalton.
2. Berzelius suggested using one or two letters of the name of the element for its symbol.
3. Earlier, the names of elements were derived from the name of the place where they were found for the first time, for example, the name copper was taken from Cyprus.
4. Some names were also taken from specific colors. For example, gold was taken from the English word meaning yellow.
5. IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) approves the names of elements.
6. The abbreviation used for the lengthy names of elements are termed as their symbols.
7. The symbol of an element is formed by writing only the first letter or first letter followed by second and some other letter of the name of that element.
For example – Nitrogen (N)
Iron (Fe)
Magnesium (Mg)
Argon (Ar)
8. While writing the symbol of an element, the first letter of a symbol is always capital (uppercase) and the second letter is smaller (lowercase).
For example – Chlorine (Cl)
Lead (Pb)
Zinc (Zn)
9. Symbols have been taken from the names of elements in Latin, German or Greek.
For example – Iron (Fe) – Latin name (Ferrum)
Sodium (Na) – Latin name (Natrium)
Atomic Mass :
1. According to the concept of Dalton's Atomic Theory, each element had a characteristic atomic mass which prompt scientists to measure the atomic mass of an atom.
2. The mass of an atom of an element is called its Atomic Mass.
3. Earlier 1/16 of the mass of an oxygen atom was used as a standard for calculating the mass of other elements.
4. However, in 1961 for a universally accepted atomic mass unit (u), carbon-12 isotope was chosen as the standard reference for measuring the atomic and molecular mass of elements and compounds.
· The Atomic Mass unit is defined as the quantity of mass equal to 1/12 of mass of an atom of carbon-12.
· 1 amu or u = 1/12 × Mass of an atom of c12
· 1 u = 1.66 × 10-27 k
· For example –
1. Hydrogen – 1 u
2. Carbon – 12 u
3. Nitrogen – 14 u
4. Oxygen – 16 u
5. Sodium – 23 u
6. Magnesium – 24 u
7. Sulfur – 32 u
8. Chlorine – 35.5 u
9. Calcium – 40 u
Atoms Existence:
Atoms of most of the elements are very reactive and hence, do not exist independently.
Noble gases are the only atoms (such as He, Ne, Kr, Xe, and Rn) are unreactive and can exist independently as a single atom.
Atoms form molecules and ion, that aggregate in large numbers to form the matter that we can see, feel, or touch.
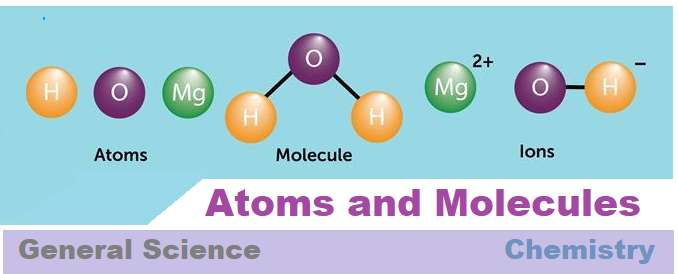
3. Molecules and ions
Molecules:
A molecule is in general a group of two or more atoms that are chemically bounded together by certain attractive forces.
For example – Two atom of hydrogen (H2) and one atom of Oxygen (O) combine with each other to form one molecule of water (H2O)
Atoms of the same element or a different element can join together to form molecules.
Molecules of Elements :
The molecules of an element are constituted by the same type of atoms.
For example – Helium (He) consists of only one atom while chlorine (Cl) consists of two atoms.
The number of atoms constituting a molecule is known as its atomicity. For example – helium is monoatomic and oxygen is diatomic.
1. Monoatomic - when an element is made up of only one atom. Ex – helium (He), all metals
2. Diatomic - when an element is made up of two atoms. Ex – oxygen (O2), all gases
3. Triatomic - when an element is made up of three atoms. Ex – ozone (O3)
4. Tetra-atomic - when an element is made up of four atoms. Ex – phosphorus (P4)
5. Poly- atomic - when an element is made up of more than two atoms. Ex – sulphur (S8)
Molecules of Compounds :
Atom of different element combines together in definite or fixed proportion to form molecules of compounds.
For example - One atom of carbon (C) and two atom of Oxygen (O2) combine with each other to form one molecule of water (CO2).
Ions:
Compounds are made up of metals and non-metals. These elements contain charged species, which are known as ions.
These are basically charged particles which can be both negatively (-) or positively (+) charged.
The element which has negatively charged ion is called an ‘anion’ and the element which has positively charged ion is called ‘cation’.
For example – NaCl , i.e., (Na+ ) ( cl -)
A group of an atom carrying a charge is called a polyatomic ion.
4. Chemical Formula of compounds and rules for writing
Chemical Formula:
The symbolic representation of composition is termed as the chemical formula of a compound.
Two things are required to learn and write chemical formula:
1. Ability to write symbols, which one can attain after good practice over learning and memorising symbols.
2. Combining capacity of the element of compound or valency.
Valency :
The combining power or capacity of an element is termed as its valency.
It helps in finding out, how the atoms of an element will combine with atom(s) of the another element to form a reaction or any chemical compound.
It can be also defined as the numbers of electrons that an atom may lose or gain during sharing of electrons or any chemical reaction to achieve noble gas configuration.
For example - the sodium ion is represented as (Na+), which means that its valency is 1. Similarly, the magnesium ion is represented as (Mg2+) which means its valency is 2.
Rules For Writing a Chemical Formula:
First step is to balance the valencies or charges on the ions.
One must write the name of a metal first, if the compound consists of a metal and a non-metal. For example- sodium chloride (NaCl), copper oxide (CuO), calcium oxide (CaO) etc.
The ion is enclosed in a bracket before writing the number of ion associated to it, in case of polyatomic ion. For example - (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4
If there is single ion then no need to mention the ions in brackets. For example – NaOH.
Rules For Writing Formula Of Simple Compound :
The simplest compounds, which are made up of two different elements are called binary compounds.
Steps to write formula of a compound –
Write the symbol of the constituent elements of the compound and their respective valencies or charges as shown below.
Crossover the valencies of the elements.
Write down the symbols with the valencies or charges which you get after crossing over.
For example –
1. The formula of water :
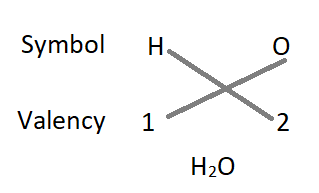 - The formula of the compound will be H2O.
- The formula of the compound will be H2O.
2. The formula of carbon tetrachloride :
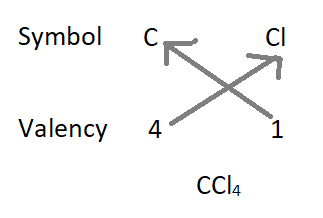 - Formula of the compound will be CCl4
- Formula of the compound will be CCl4
3. Formula of aluminium oxide :
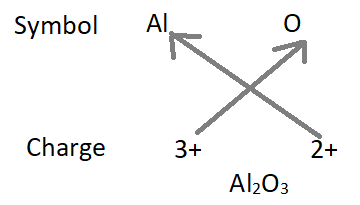 - Formula of the compound will be Al2O3
- Formula of the compound will be Al2O3
4. Formula of ammonium sulfate:
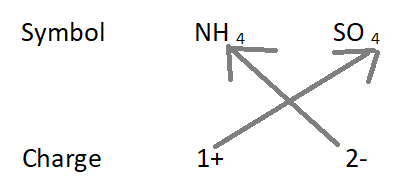 The formula of the compound will be (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4
The formula of the compound will be (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4
5. Molecular Mass and Mole Concept
The summation of the atomic masses of all the atoms in a molecule of the substance is known as the molecular mass of that substance. It is expressed in atomic mass units (AMU) or (u).
For example – the molecular mass of H 2 O will be calculated as :
The atomic mass of hydrogen = 1 u,
Atomic mass of oxygen = 16 u
Thus,
The molecular mass of water which contains two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of Oxygen is
= ( 2 × 1 ) + (1 × 16)
= 18 u
Formula Unit Mass
The summation of the atomic masses of all atoms in a formula unit of a compound is known as the formula unit mass of a substance.
It can be calculated in the same way as we do to calculate the molecular mass.
The difference between calculating the molecular mass and calculating the formula unit mass is just that we use the word formula unit for those substances whose constituent particles are ions.
For example - the formula unit mass of (CaCL 2) can be calculated as –
= Atomic mass of Ca + (2 × atomic mass of Cl)
= 40 + 2 × 35.5
= 40 + 71
= 111 u
Mole concept :
Interpreting chemical equation :
For instance –
2H 2 + O 2 - 2H 2 O ( reaction of hydrogen and water to form water )
1. We can say that two molecules of hydrogen combine with one molecule of oxygen to form two molecules of water, or
2. We can also say that 4u of hydrogen molecules combine with 32u of oxygen molecules to form 36u of water molecules.
Here, we have concluded that a substance can be characterized by its mass or the number of molecules.
Therefore, we can find conclusion from the above reaction and concerning procedures that it is more convenient to refer to the quantity of a substance in terms of the number of its molecules or atoms, rather than their masses.
This interpretation results in a new unit “mole”
Mole :
It can be defined as the quantity in numbers having a mass equal to its atomic or molecular mass in grams of any species (atoms, molecules, ions, or particles).
The number of particles (atoms, molecules, and ions) present in 1 mole of any substance is fixed, having a value of 6.022 × 10 23 .
The number 6.022 × 10 23 is an experimentally obtained value which is also known as Avogadro constant or Avogadro number, represented by No.
This value is named in honor of the Italian scientist, Amedeo Avogadro.
Mass of 1 mole of a substance is known as its molar mass. Everything will be just the same as that of atomic or molecular mass, we just need to change the unit from 'u' to 'g'.
For example -
The atomic mass of sulphur is 32 u but the gram Atomic mass is 32 g.
The molar mass of atoms is also known as gram atomic mass.
Gram Atomic Mass - the atomic mass of a substance when expressed in grams is known as its gram atomic mass.
For example –
The atomic mass of hydrogen = 1 u
So, the gram atomic mass of hydrogen = 1 g
Gram Molecular Mass – the molecular mass of a substance when expressed in grams is known as its gram molecular mass.
For example -
1 u hydrogen = 1 atom of hydrogen
1 g hydrogen = 1 mole atom, i.e.,
6.022 × 10 23 atoms of hydrogen.
In the case of any chemical equation, the mole is used as the measuring unit.
Wilhelm Ostwald introduced the word 'mole' in 1896 from the Latin word moles meaning a 'pile' or 'heap'.
The unit “mole” was accepted in 1967.
No. of moles \( = { given \ mass \over molar \ mass } \)
No. of moles \( = { given \ number \ of \ particles \over Avogadro \ number } \)
Mass = molar mass × number of moles
The number of atoms \( = { given \ mass \over molar \ mass } \) × Avogadro number
The number of Molecules \( = { given \ mass \over molar \ mass } \) × Avogadro number
More in this Chapter..

Laws Of Chemical Combination And Dalton's Atomic Theory
Lavoisier and Joseph L. Proust proposed two laws of chemical combination. during a chemical reaction, the sum of masses of the reactant and the pro
4.37M Join the discussion.

Atom, Atomic Mass, Atoms Existence And Nomenclature Of Elements
Atoms are extremely small, they are smaller than anything that we can imagine or compare with.For example – more than millions of atoms when stacked
4.37M Join the discussion.

Molecules and ions
A molecule is, in general, a group of two or more atoms that are chemically bounded together by certain attractive forces. For example, Two atom of
4.37M Join the discussion.

Chemical Formula of compounds and rules for writing
The symbolic representation of composition is termed as the chemical formula of a compound. Two things are required to learn and write a chemical f
4.37M Join the discussion.

Molecular Mass and Mole Concept
The summation of the atomic masses of all the atoms in a molecule of the substance is known as the molecular mass of that substance. It is expresse
4.37M Join the discussion.
.png)


















.jpg)








 संज्ञा
संज्ञा  Profit And Loss, Basic Tricks And Examples
Profit And Loss, Basic Tricks And Examples