“Sonar” can be defined as “Sound Navigation and Ranging”.
This device is used to measure the distance, direction, and speed of an underwater object by using the same ultrasonic waves.
It consists of two major devices – a transmitter and a detector ( or receiver).
It is usually fixed or installed in a boat or ship for their safety purpose.
The transmitter is used to produce and transmit ultrasonic waves that travel through water and after striking any objects on the seabed it gets reflected back and is sensed by the detector.
The detector is used to convert ultrasonic waves into electrical signals which are then appropriately interpreted.
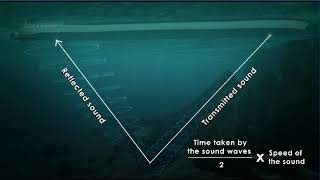
The distance of the object can be calculated by knowing the speed of the sound in water and the time interval between the transmission and reception of the ultrasound. This phenomenon is known as “Echo-Ranging”.
The formula to calculate the distance of the object is 2d = v × t.
Thus, this technique is used to determine the depth of the sea and to locate underwater hills, submarines icebergs, valleys, sunken ships, etc.
How Do Bats Search Their Prey?
.png)

















.jpg)







