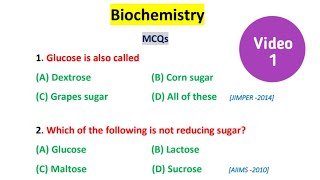
This is the second practice test in biochemistry. It is prepared in the view of diploma 1st year students but it will be helpful for every biochemistry student. Attempting this test will help to understand and revise some basic topics in biochemistry either preparing for entrance exams, final exams or for competitive exams.
Please must refer your textbooks and must read the topics arrived in these MCQs.