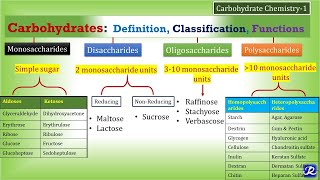
This post includes Important one-liner Questions from the chapter – Carbohydrates which precisely summarise the chapter Carbohydrates (biomolecules) in Biochemistry.
Biochemistry Important one liner Questions on carbohydrates
1
The and cyclic forms of D-glucose are referred to as
Anomers
2
If two monosaccharides differ in configuration around a single carbon atom, they are known as
Epimers
3
The carbohydrate that is taken as a reference for writing the configuration of others
Glyceraldehydes
4
Name a non-reducing disaccharide
Sucrose
5
The non-carbohydrate moiety found in glycosides is known as
Aglycone
6
Give an example of a glycoside antibiotic
Streptomycin
7
The glycosidic bonds at the branching points in the structure of starch are
1,6- glycosidic bond
8
The polysaccharide employed for the assessment of kidney function
Insulin
9
The glycosaminoglycan that serves as a lubricant and shock absorbant of joints
Hyaluronic acid
10
Name the sialic acid, mostly found in the structure of glycoproteins and glycolipids
N- Acetylneuraminic acid
11
Carbohydrates are the polyhydroxyaldehydes or ketones, or compounds which produce them on
Hydrolysis
12
The major dietary energy sources, besides their involvement in cell structure and various other functions is
Carbohydrates
13
The most important naturally occurring aldose/monosaccharide.
D- glucose
14
The polymers of monosaccharides or their derivatives, held together by glycosidic bonds
Polysaccharide
15
The carbohydrate reserves of plants
Starch