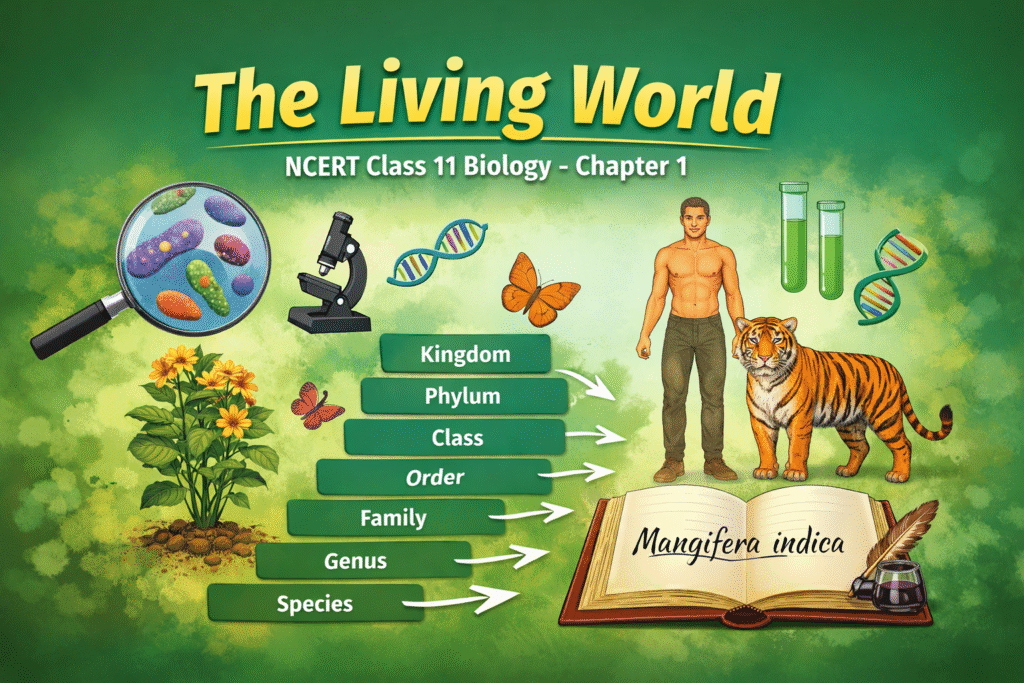
NCERT Class 11 Biology Chapter 1 “The Living World” important questions and answers covering classification of organisms, taxonomical hierarchy, scientific nomenclature, species concept, and taxa. Clear, exam-oriented answers prepared strictly as per the latest NCERT syllabus for CBSE Class XI Biology students.
Question No. 5
Given below is the scientific name of Mango. Identify the correctly written name.
Mangifera Indica
Mangifera indica
Answer: Mangifera indica
Explanation: In scientific nomenclature, the generic name begins with a capital letter, the specific epithet begins with a small letter, and both words are written in italics or underlined separately.
Question No. 7
Can you identify the correct sequence of taxonomical categories?
(a) Species → Order → Phylum → Kingdom
(b) Genus → Species → Order → Kingdom
(c) Species → Genus → Order → Phylum
Answer: (c) Species → Genus → Order → Phylum
Question No. 9
Define the following terms:
(i) Phylum: A group of related classes that share basic structural and organisational similarities.
(ii) Class: A group of related orders having common characteristics.
(iii) Family: A group of related genera with more similarities than differences.
(iv) Order: A group of related families.
(v) Genus: A group of closely related species.
Question No. 10
Illustrate the taxonomical hierarchy with suitable examples of a plant and an animal.
Example 1: Plant (Mango)
Kingdom : Plantae
↓
Division : Angiospermae
↓
Class : Dicotyledonae
↓
Order : Sapindales
↓
Family : Anacardiaceae
↓
Genus : Mangifera
↓
Species : Mangifera indica
Example 2: Animal (Human)
Kingdom : Animalia
↓
Phylum : Chordata
↓
Class : Mammalia
↓
Order : Primates
↓
Family : Hominidae
↓
Genus : Homo
↓
Species : Homo sapiens
Questions and Answers
Q1. Why are living organisms classified?
Answer:Living organisms are classified to make their study easier and systematic. Classification helps in identification, understanding similarities and differences among organisms, studying their evolutionary relationships, and ensuring uniformity in scientific communication worldwide.
Q2. Why are the classification systems changing every now and then?
Answer:Classification systems keep changing due to the discovery of new organisms and the development of new techniques such as molecular biology and genetic analysis. Improved understanding of evolutionary relationships has also led to revisions in existing classification systems.
Q3. What different criteria would you choose to classify people that you meet often?
Answer:People can be classified based on various criteria such as age, sex, profession, educational background, language spoken, place of residence, and lifestyle habits.
Q4. What do we learn from identification of individuals and populations?
Answer:Identification helps in recognizing organisms correctly, understanding their characteristics, distribution, population structure, evolutionary relationships, and ecological roles. It is essential for biodiversity studies and conservation planning.
Q5. Q6. Define a taxon. Give some examples of taxa at different hierarchical levels.
Answer:A taxon is a taxonomic group of any rank in the classification system.
Examples of taxa at different levels:
Kingdom: Animalia,
Phylum: Chordata,
Class: Mammalia,
Order: Primates,
Family: Hominidae,
Genus: Homo,
Species: Homo sapiens
Q6. Q8. What is meant by the term ‘species’? Discuss its meaning in higher plants and animals and in bacteria.
Answer:A species is the basic unit of classification, defined as a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring under natural conditions.
In higher plants and animals: Species are defined based on reproductive isolation and the ability to interbreed.
In bacteria: Since reproduction is asexual, species are defined based on genetic similarity, biochemical characteristics, and DNA homology.
Q7. Why are living organisms classified?
Answer:Living organisms are classified to make their study easier and systematic. Classification helps in identification, understanding similarities and differences among organisms, studying their evolutionary relationships, and ensuring uniformity in scientific communication worldwide.
Q8. Why are the classification systems changing every now and then?
Answer:Classification systems keep changing due to the discovery of new organisms and the development of new techniques such as molecular biology and genetic analysis. Improved understanding of evolutionary relationships has also led to revisions in existing classification systems.
Q9. What different criteria would you choose to classify people that you meet often?
Answer:People can be classified based on various criteria such as age, sex, profession, educational background, language spoken, place of residence, and lifestyle habits.
Q10. What do we learn from identification of individuals and populations?
Answer:Identification helps in recognizing organisms correctly, understanding their characteristics, distribution, population structure, evolutionary relationships, and ecological roles. It is essential for biodiversity studies and conservation planning.
Q11. Q6. Define a taxon. Give some examples of taxa at different hierarchical levels.
Answer:A taxon is a taxonomic group of any rank in the classification system.
Examples of taxa at different levels:
Kingdom: Animalia,
Phylum: Chordata,
Class: Mammalia,
Order: Primates,
Family: Hominidae,
Genus: Homo,
Species: Homo sapiens
Q12. Q8. What is meant by the term ‘species’? Discuss its meaning in higher plants and animals and in bacteria.
Answer:A species is the basic unit of classification, defined as a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring under natural conditions.
In higher plants and animals: Species are defined based on reproductive isolation and the ability to interbreed.
In bacteria: Since reproduction is asexual, species are defined based on genetic similarity, biochemical characteristics, and DNA homology.